Safe Steps, Sound Homes: Understanding Porch Step Handrail Codes
Is your porch a welcoming haven or a potential hazard? While aesthetics and comfort are important, safety should be the cornerstone of any porch design. A crucial aspect of porch safety lies in adhering to porch step handrail codes. Understanding these regulations is not just about compliance; it’s about protecting yourself, your family, and your guests from preventable accidents.
Porch step handrail regulations provide a framework for constructing safe and accessible entrances. These codes, often adopted at the local or state level, dictate specific requirements for handrail height, materials, and structural integrity. While variations may exist depending on your location, the underlying principle remains constant: to minimize the risk of falls and ensure safe navigation of porch steps.
The history of handrail regulations is intertwined with the evolution of building codes. As construction practices advanced and safety awareness grew, the need for standardized guidelines became apparent. Initially, these codes focused on structural integrity, but over time, they expanded to encompass accessibility and usability, particularly for individuals with mobility challenges. The current emphasis on porch step handrail code reflects a broader societal commitment to universal design principles.
Ignoring porch step handrail codes can lead to several significant problems. From a safety perspective, the absence of proper handrails increases the likelihood of falls, particularly for children, the elderly, and individuals with disabilities. From a legal standpoint, non-compliance can result in fines, penalties, and even legal liability in the event of an accident. Furthermore, failing to meet code requirements can negatively impact property value and complicate future renovations or sales.
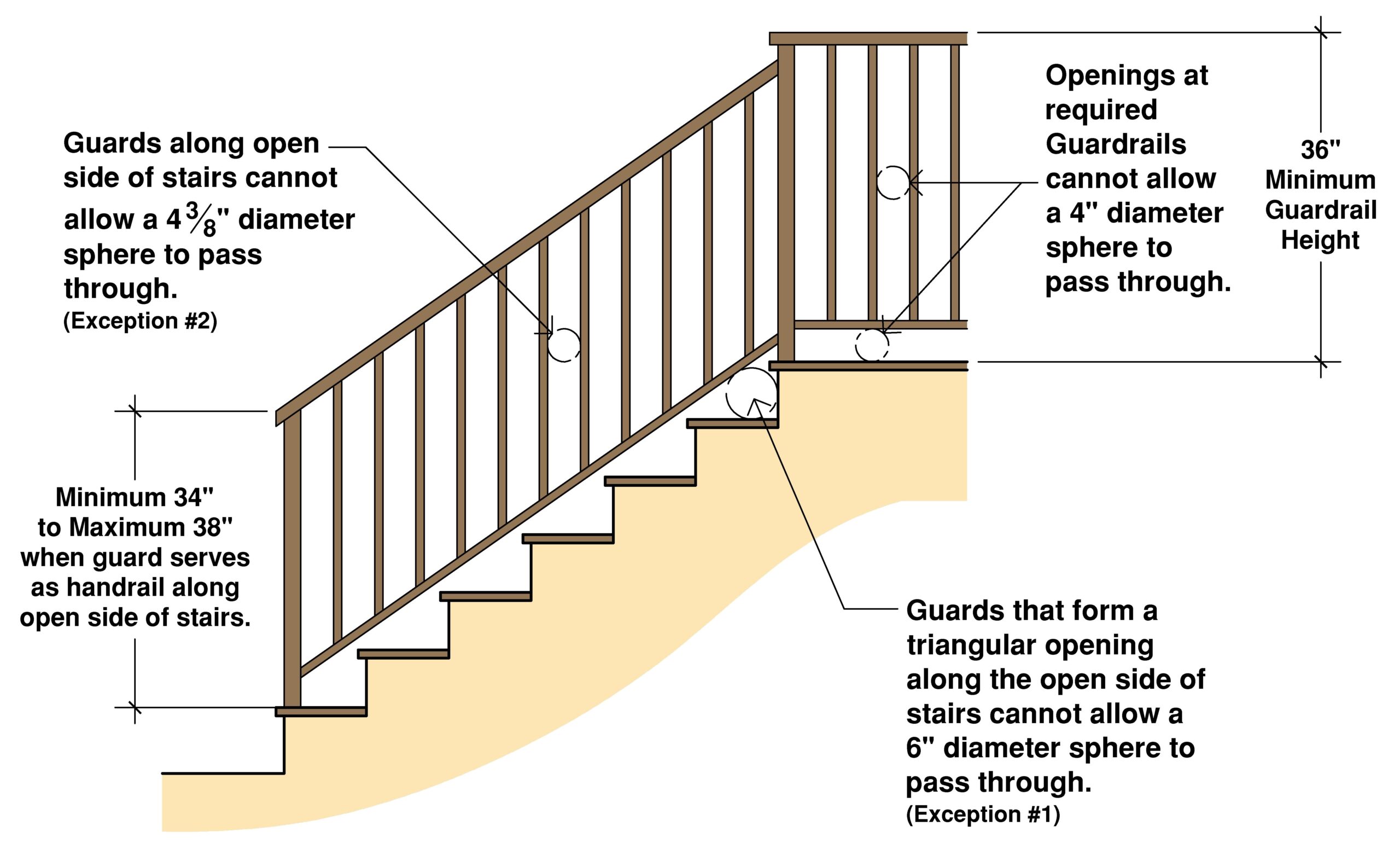
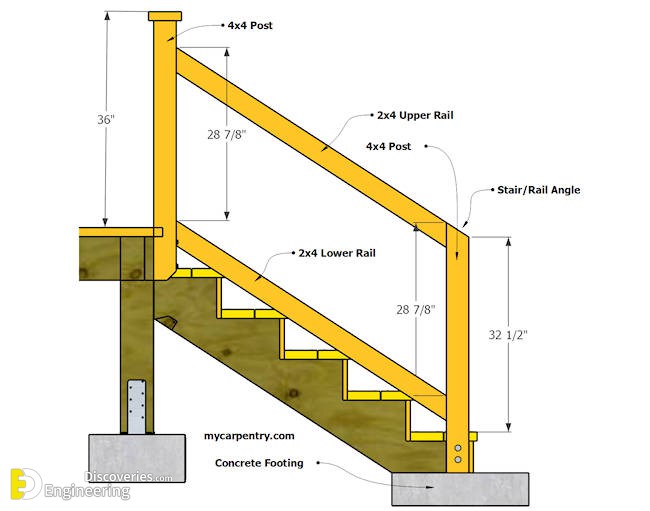
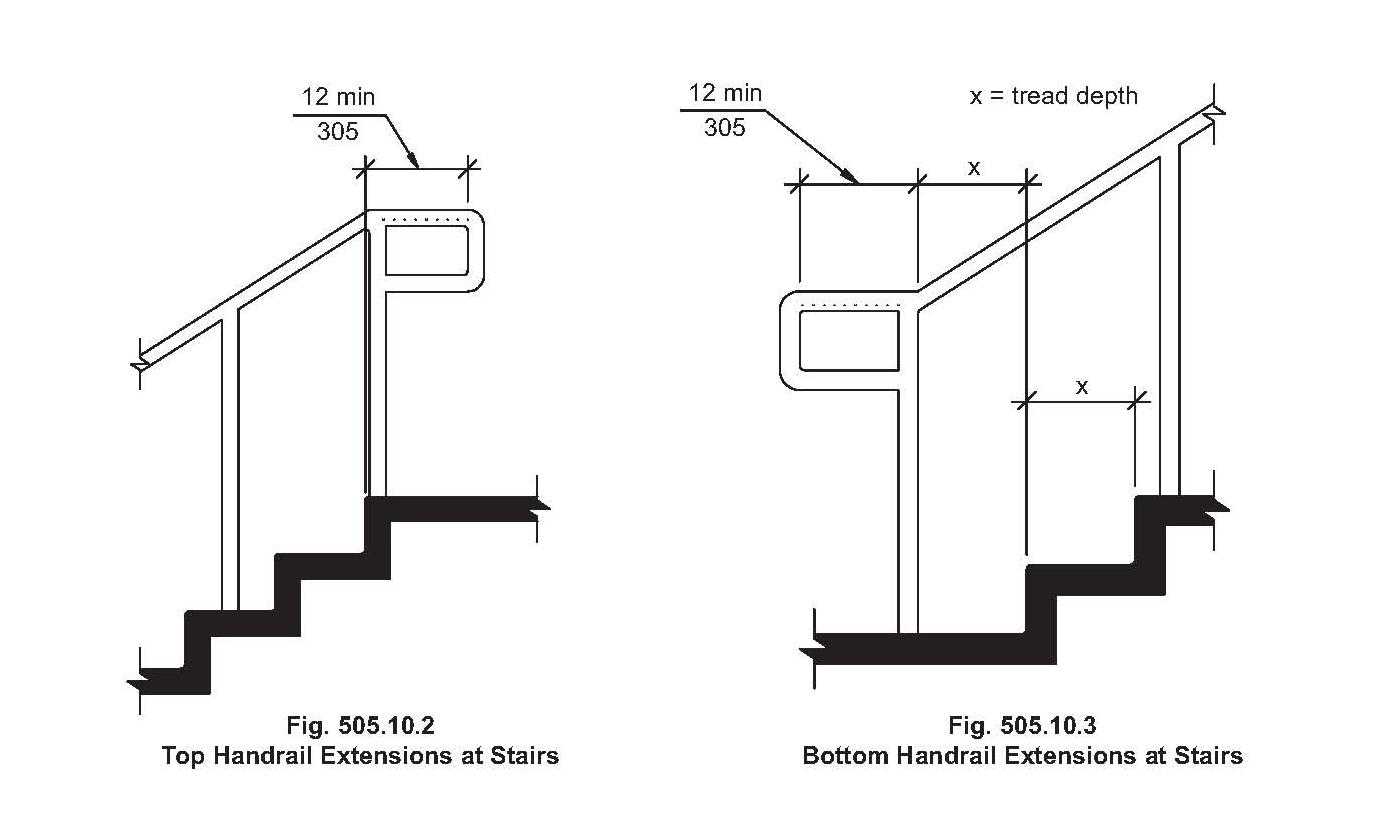
Handrail regulations typically specify minimum and maximum heights, acceptable materials, and load-bearing capacity. For instance, a common requirement is a handrail height between 34 and 38 inches, measured vertically from the nosing of the stair tread. Materials must be sturdy and weather-resistant, such as wood, metal, or composite materials. These specifications are designed to provide a secure and comfortable grip, regardless of weather conditions or individual abilities.
One key benefit of following handrail codes is enhanced safety. Properly installed handrails offer stability and support, reducing the risk of slips and falls. Another advantage is improved accessibility. Handrails make it easier for individuals with mobility limitations to navigate stairs, promoting independence and inclusion. Furthermore, compliance with building codes enhances the overall value and marketability of a property.
Before embarking on any porch construction or renovation project, consult your local building department to obtain the specific handrail code requirements for your area. Next, carefully measure your porch steps and plan your handrail installation accordingly. Choose appropriate materials and ensure that the handrails are securely fastened to provide adequate support. Finally, have a qualified inspector verify that your installation meets all applicable codes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Handrail Codes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Safety | Potential Cost Increase |
| Improved Accessibility | Design Limitations in Some Cases |
| Enhanced Property Value | Code Variations Can Be Confusing |
Best Practices:
1. Consult local codes.
2. Use durable materials.
3. Ensure secure fastening.
4. Maintain handrails regularly.
5. Consider lighting for enhanced safety.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the standard handrail height? (Answer: Typically between 34 and 38 inches.)
2. What materials can be used for handrails? (Answer: Wood, metal, composite.)
3. Are handrails required on all porches? (Answer: Depends on local codes and number of steps.)
4. How do I find my local building codes? (Answer: Contact your local building department.)
5. Can I install handrails myself? (Answer: Yes, but professional installation is recommended.)
6. What is the penalty for not having handrails? (Answer: Varies depending on location, can include fines.)
7. How often should handrails be inspected? (Answer: Regularly, especially after harsh weather.)
8. Where can I find more information on handrail codes? (Answer: Local building codes, online resources.)
Tips and Tricks: Use contrasting colors for handrails to improve visibility. Consider adding non-slip material to handrail surfaces for added grip. Regularly inspect and maintain handrails to ensure long-term safety and durability.
In conclusion, porch step handrail codes are vital for ensuring the safety and accessibility of our homes. By understanding and adhering to these regulations, we create environments that are welcoming and hazard-free. The benefits of proper handrail installation extend beyond mere compliance; they contribute to a greater sense of security, enhance property value, and foster a culture of universal design. Taking the time to research and implement appropriate handrail solutions is an investment in the well-being of ourselves and those we care about. Don't compromise on safety; make your porch a secure and inviting space for everyone by prioritizing compliance with porch step handrail codes. Start by contacting your local building department today and take the first step towards a safer and more accessible home.
Mastering hvac vacuum techniques
Exploring the world of animated father and son relationships
Love profile pictures expressing affection online




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stair-handrail-and-guard-code-1822015-final-CJ-01-157768d7ac40439da36f9ba69faa00c6.png)